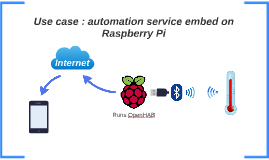
use case
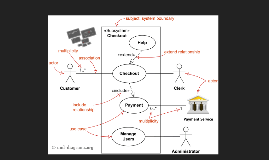
Transcript: Prototypes and Use Cases in system design Prototype Prototype A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to evaluate a new design to enhance precision by system analysts and users. Rapid throwaway Prototype Rapid Throwaway prototype is based on the preliminary requirement. It is quickly developed to show how the requirement will look visually. The customer's feedback helps drives changes to the requirement, and the prototype is again created until the requirement is base lined. Evolutionary Prototyping evolutionary Prototype Here, the prototype developed is incrementally refined based on customer's feedback until it is finally accepted. It helps you to save time as well as effort. That's because developing a prototype from scratch for every interaction of the process can sometimes be very frustrating. Incremental Prototyping incremental Prototype In incremental Prototyping, the final product is decimated into different small prototypes and developed individually. Eventually, the different prototypes are merged into a single product. This method is helpful to reduce the feedback time between the user and the application development team. Extreme Prototyping Extreme prototype Extreme prototyping method is mostly used for web development. It is consists of three sequential phases. Basic prototype with all the existing page is present in the HTML format. You can simulate data process using a prototype services layer. The services are implemented and integrated into the final prototype. Best Practices Best Practices You should use Prototyping when the requirements are unclear. It is important to perform planned and controlled Prototyping. Regular meetings are vital to keep the project on time and avoid costly delays. The users and the designers should be aware of the prototyping issues and pitfalls. Pros and Cons Pros and Cons Pros Pros it helps communication help reduce risk errors can be detected easily less software rejection identify what is missing straight forward model Cons Cons slow and time consuming cost is a total waste since prototypes are thrown away excessive changes request customers are not willing to participate from time to time requirement can change poor documentation misunderstanding can happen in early in the prototype stage What is use case Use cases once specified can be denoted both textual and visual representation (i.e. use case diagram). Use cases Use case Use case System function (process - automated or manual) Named by verb + Noun (or Noun Phrase). i.e. Do something Each Actor must be linked to a use case, while some use cases may not be linked to actors. Actor Actor Someone interacts with use case (system function). Named by noun. Actor plays a role in the business Similar to the concept of user, but a user can play different roles For example: A prof. can be instructor and also researcher plays 2 roles with two systems System System The system boundary is potentially the entire system as defined in the requirements document. For large and complex systems, each module may be the system boundary. Pros & Cons Pros & Cons Use cases can serve as the basis for the estimating, scheduling, and validating effort. Use cases have proved to be easily understandable by business users, and so have proven an excellent bridge between software developers and end users. Visualization. Pros Cons Time-consuming to generate. Require the co-existence of prototypes. They do not capture the non-functional requirements easily System design System design & Example System design is the process of designing the elements of a system such as the architecture, modules and components, the different interfaces of those components and the data that goes through that system. Example